
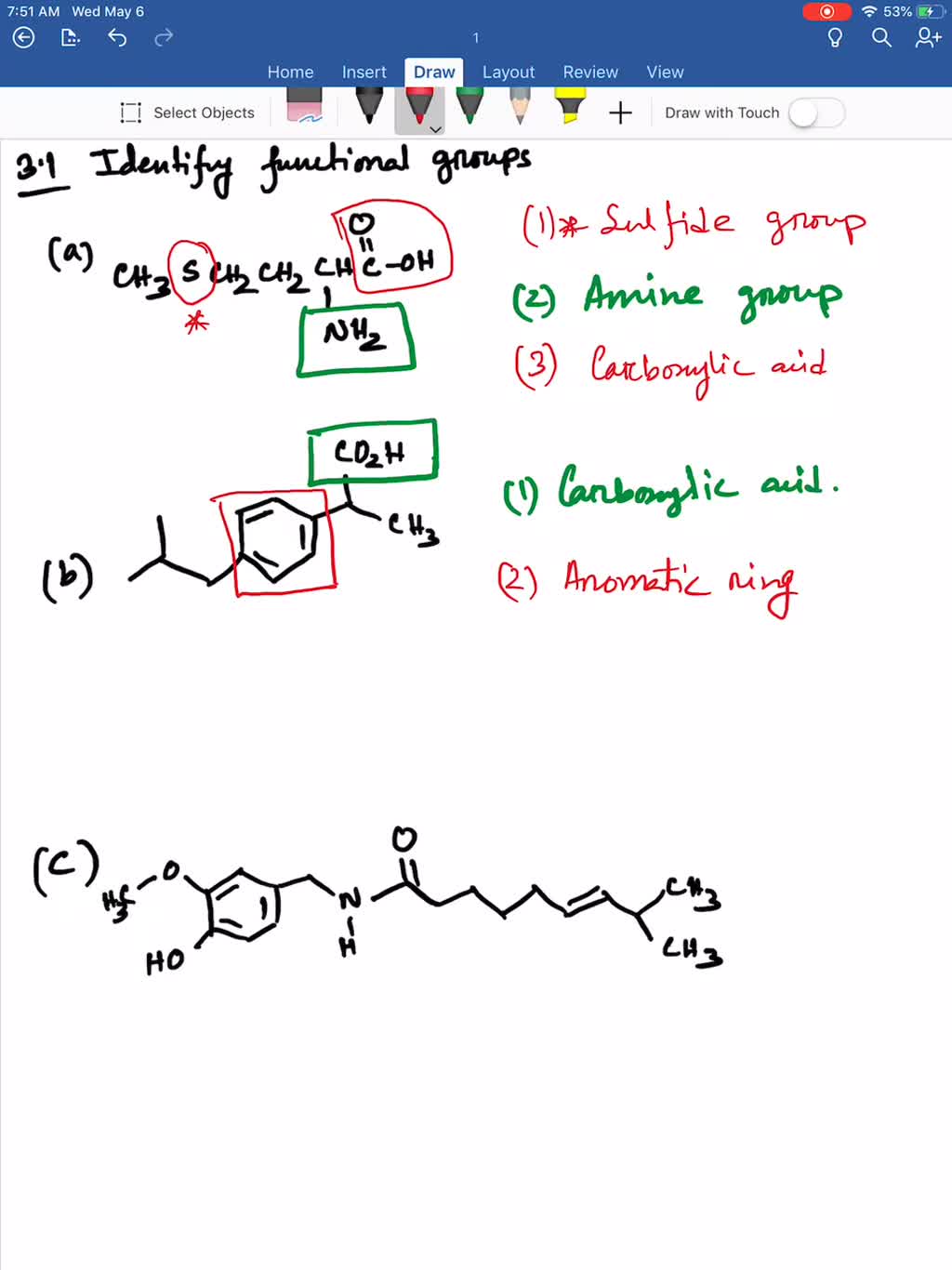
From the IUPAC convention, the one with greater priority is carboxylic acid derivatives which include amides also.

Priority Order of Functional Groups in IUPACįor representing the position where the functional group is attached a priority order is necessary when a compound contains more than one functional group. For organic chemistry, functional groups are very important. When the functional group is attached to a carbon that carbon is called alpha and the nearby carbon as beta and consequently gamma for the next carbon atom are also given. Depending on the position where the functional group is attached certain other names are also included. The reactivity of a particular functional group can be explained by using some other factors. By giving different names to a particular functional group made the distinction of organic compounds easy. Properties of phenol and benzenes are extremely different.įigure showing the structure of phenol Functional Groups Chemistryįunctional groups play a great role in many fields of organic chemistry. For example, benzene and phenol where an OH group is attached to the molecule. And the new compound formed has property entirely different from the parent molecule. The groups of atoms or substituent or moiety get attached to an organic compound and thereby changing the whole molecule’s chemical and physical properties. If it contains only a single carbon atom can be named methylamine and if it contains two carbon atoms it is named dimethylamine and if it is 3 it is trimethylamine. Depending on the number of carbon atoms present the naming also varies. These are means may be primary, secondary, and tertiary as well. These compounds are given the common name amine represented by NH 2. The functional groups that contain nitrogen atoms are nitrogen-containing functional groups. Amide is an example where it contains nitrogen also. There are various types of functional groups containing carbon-oxygen bonds so the naming also varies with the type of atom to which it is attached. The reactivity is also very is with the presence of a bond between them. The bond present on them may be a double bond that is SP 2 hybridization and a single bond SP 3 hybridized. The functional group which contains an oxygen atom is the oxygen-containing functional group. Except for alkyl fluorides, all other haloalkanes undergo elimination and nucleophilic substitution reactions. For example, the carbon-fluorine bond is highly strong and highly stable compared to the carbon-iodine bond. Depending on the type of halogen present on them the stability and the strength of these bonds change.
An example of this is CH 3Cl with the name methyl chloride. For the notation of this species, the name ‘halo’ is used. It is also present in the charged ions and uncharged form charged hydrocarbons are called carbocations with a positive charge and carbanions with a negative charge.Īlkyl halides are functional groups that contain carbon and halogen bond. And also reactivity depends on whether it is cyclic or acyclic. The reactivity of these types of compounds is a dependent bond present in between the carbon atom that is a double or triple bond. Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and benzene are some of the functional groups in hydrocarbons these are generally represented by the simple R. Those functional groups that are hydrocarbons when they contain hydrogen and carbon atom. Some of the functional groups are described below. The presence of certain functional groups on a molecule also affects its solubility for example sugar is a molecule that contains OH group attached to it and is easily dissolvable in water which means that when a highly electronegative group here oxygen is get attached to a less electronegative atom or molecule hair hydrogen the polarity increases and thereby the solubility in water increases. Functional groups are ligands when it gets bonded to a coordination complex that is forming a coordination bond with metal atoms. And uncharged molecules do not contain a charge on them example OH functional group. Functional groups that contain any of the charges that are positive or negative are common one such example is COO - that is carboxylate. Functional groups can be charged for uncharged.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
